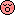
The stinging, venom-filled nematocysts[13] in the tentacles of the Portuguese man o' war can paralyze small fish and other prey. Detached tentacles and dead specimens (including those that wash up on shore) can sting just as painfully as the live creature in the water and may remain potent for hours or even days after the death of the creature or the detachment of the tentacle.[14]
Stings usually cause severe pain to humans, leaving whip-like, red welts on the skin that normally last 2 or 3 days after the initial sting, though the pain should subside after about an hour. However, the venom can travel to the lymph nodes and may cause, depending on the amount of venom, a more intense pain.[citation needed] A sting may lead to an allergic reaction. There can also be serious effects, including fever, shock, and interference with heart and lung function. Stings may also cause death,[15] although this is extremely rare. Medical attention may be necessary, especially if pain persists or is intense, there is an extreme reaction, the rash worsens, a feeling of overall illness develops, a red streak develops between swollen lymph nodes and the sting, or either area becomes red, warm and tender.